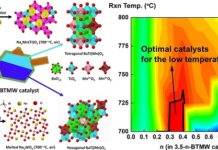
India is set to develop its own versions of small reactors, bolstered by increased government funding and private sector participation, aiming to expand its nuclear power capabilities as part of its clean energy initiative to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070.
Government support for emerging technology will foster partnerships between Indian public or private entities and various foreign companies interested in the Indian market. The budget has identified these proposed indigenous reactors as Bharat Small Reactors and Bharat Small Modular Reactors. Government funds will be allocated for research and development in new nuclear technologies. The small reactors are a variant of small modular reactor (SMR) technology.
The government aims to increase nuclear power capacity to support carbon mitigation efforts. Traditional nuclear plants of 1,000 MWe require extensive engineering and construction, face land availability issues, and encounter opposition from local populations due to safety concerns. In contrast, the world nuclear association describes SMRs as reactors with a capacity of 300 MW or less, featuring a modular design.
The design enables factory fabrication, leveraging economies of scale, resulting in shorter construction times and easier transportation. The modular design allows these plants to operate in off-grid mode or remote areas and provides operational flexibility for improved load management.
As reported by msn.com, the factory fabricated reactors can be transported by trucks or rail to a nuclear power site, and their output can be scaled by combining several units to achieve larger capacities.